What is a pressure transmitter?
What is a pressure transmitter?
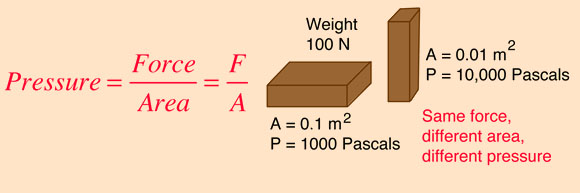
What is a pressure transmitter? A pressure transmitter or pressure sensor is a device that measures pressure in a liquid, fluid, or gas, or level of industrial liquids and gases.
Transmitter use to measure pressure in different processes.
Pressure transmitters are divided into three types:
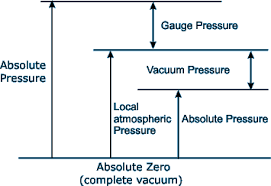
Absolute Transmitter:
Absolute transmitter takes vacuum pressure as its base and then measures process pressure.
Gauge Transmitter:
This type measures process pressure with the location’s atmospheric pressure as a base.
Differential Transmitter:
When sensing units are introduced to multiple pressures as inputs, differential transmitters measure the differences between the various pressures.
Then it’s transducing that pressure into an analog electrical signal.
There are various types of pressure transducers, such as:
- Pneumatic transmitter
- Analog transmitter
- Digital transmitter
Transducer
A transducer is a device which measures a physical quantity such as temperature or pressure and converts it into an electrical output signal.
What is the difference between transmitter and transducer
Both transducers and transmitters convert energy from one form to another and give an output signal. The signal is directed to any device that interprets it and uses it to display a record or alter the pressure in a system.
So how do you decide whether it is best to use a transducer or transmitter for your application? Transducers and transmitters are virtually the same things, the main difference being the kind of electrical signal each sends.
A transducer sends a signal in volts (V) or millivolt (mV) and a transmitter sends a signal in milliamps (mA).
If the electrical connections in your process are short, such as in the laboratory or inside an electronics enclosure, a pressure transducer is more desirable as they tend to be smaller and there are very few active electronic components that can be upset by electromagnetic interference.
HART®
HART or Highway Addressable Remote Transducer is a type of digital communications protocol for configuring and reading instrumentation via the 4 to 20mA current loop. HART® data is communicated via a low-level AC digital signal which is superimposed on a 2 wire 4-20mA current loop signal and functions simultaneously without interfering with the measurement output signal.