What is Pressure?
What is Pressure?
What is pressure ? pressure is defined as force per unit area.
At first, we explain the concept of Pressure in Science, Physics, and Chemistry.
Pressure, in the physical sciences, the perpendicular force per unit area, or the stress at a point within a confined fluid. … In SI units, the pressure is measured in pascals; one pascal equals one newton per square meter. Atmospheric pressure is close to 100,000 pascals.
PRESSURE is a force exerted by the substance per unit area on another substance. The pressure of a gas is the force that the gas exerts on the walls of its container.
In other words, The rapid motion and collisions of molecules with the walls of the container causes pressure (force on a unit area). Pressure is proportional to the number of molecular collisions and the force of the collisions in a particular area.
The more collisions of gas molecules with the walls, the higher the pressure.
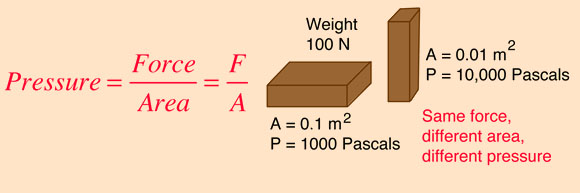
So to create a large amount of pressure, you can either exert a large force or exert a force over a small area (or do both).
This force can be exerted by liquids, by gases or vapors, or by solid bodies.
Surface compression takes place at the interface between two solid bodies, but for our purposes, we can consider this additional force negligible.
Common Units of Pressure
There are three general classifications for units of measurement as follows:
Customary (inch, pound force, second, ampere)- used primarily in English speaking countries, but in many countries are being replaced by SI units. Customary units of pressure include PSI, in. Hg, in.H2O.
SI – (meter, Newton, second, ampere) – Commonly used in Europe and now popularly known as “metric” units. SI units of pressure include bar, mbar, Pa, kPa, MPa, and N/m2.
MKSA (meter, kilogram-force, second, ampere) – formerly known as “metric” units but are generally
being replaced by SI units. MKSA units of press include kg/cm2, mH2O, mmHg, and torr.
In meteorology, an atmosphere equals 14.7 pounds per square inch or 101.325 kilopascals.
Fluid Pressure
The press exerted by a static fluid depends only upon the depth of the fluid, the density of the fluid, and the acceleration of gravity.
The pressure in a static fluid arises from the weight of the fluid and is given by the expression
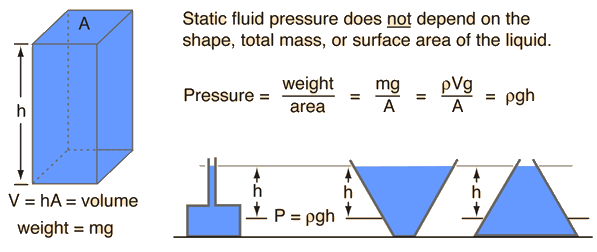
| Pstatic fluid = ρgh where | ρ = m/V = fluid density g = acceleration of gravity h = depth of fluid |
When a fluid is at rest, it exerts a force perpendicular to any surface in contact with it. This force, which is due to the continuous, random motion of molecules, is known as fluid press. Knowing the fluid pressure is essential to mechanical and hydraulic systems that use fluids move pistons and other parts.
It is usually measured in Pascals (Pa), where one Pascal is equal to one Newton per square meter (N/m2).
The fluid press is independent of the mass of the fluid but can be calculated with the density and height of the fluid.
Because of the ease of visualizing a column height of a known liquid, it has become common practice to state all kinds of pressures in column height units, like mmHg or cm H2O, etc. Press is often measured by manometers in terms of liquid column height.
Definition of Gas Press
When the molecules of gas bounce off the walls of their container, they exert a force.
The gas press is defined as the force per unit area produced by the gas. Depending on the purpose of the measurement, different units are commonly used.
The pressure gauge is an instrument that can measure the pressure of the media.
Many kinds of pressure gauges are in the industry and we can choose them according to many factors that we will talk about them in the next articles.
Saba Dejlah will offer you many kinds of gauge from the best brands in the UAE, such as WIKA, ASHCROFT,…





Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!