Pinch Valve Advantage and Disadvantage
Pinch Valve Advantage and Disadvantage
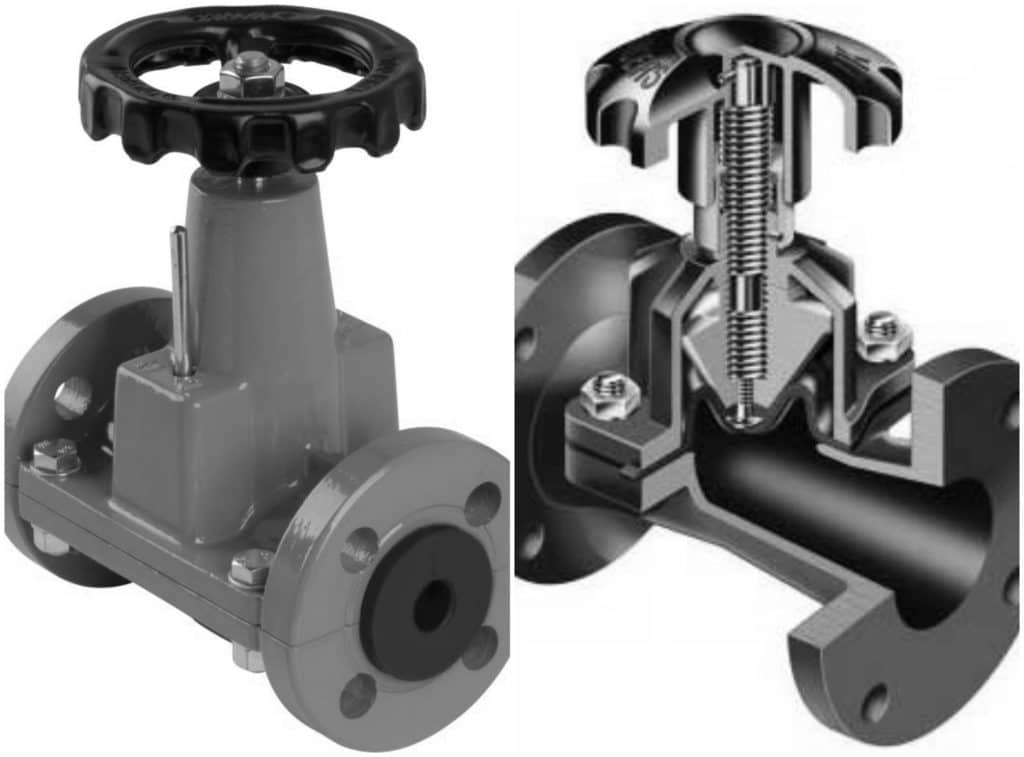
Pinch Valve is made using a metal frame that houses a rubber wear sleeve and a shut-off mechanism. The rubber sleeve is the only part that comes in contact with the flowing media; this significantly minimizes the chances of contamination within the system.
Depending on the application, the rubber sleeve is hand-built with different kinds of rubber compounds to make it suitable for the required application. Pinch valves have a full bore design with no mechanical parts and quick closing mechanism. They require little to no maintenance, additionally changing the rubber sleeve is very easy.
Relatively inexpensive linear motion pinch valve consists of a flexible tube (rubber tubing) that is mechanically pinched from the outside of the valve body.
Pinch valves are suitable for on-off and throttling services. However, the effective throttling range is usually between 10% and 95% of the rated flow capacity. Pinch valves are ideally suited for the handling of slurries, liquids with large amounts of suspended solids, and systems that convey solids pneumatically.
Because the operating mechanism of the valve is completely isolated from the fluid, these valves also find application where corrosion or metal contamination of the fluid might be a problem.
 Pinch valves benefits
Pinch valves benefits
Some of the benefits of pinch valves are:
- Minimal turbulence
- Low maintenance
- Excellent drainage
- Very Clean
- Low weight
- Inexpensive
- Low airborne contaminants
Pinch valves are preferred over other types of valves because of their low cost, easy maintenance, and full bore design offering zero leakage. They can be used in a diverse range of applications.
Advantages of Pinch Valve
- It can be used for application where corrosion or metal contamination of the fluid might be a problem. Flow from the valve is straight without any obstruction.
- There are no internal moving parts in contact with the fluid hence, low maintenance cost.
- Inexpensive due to simple construction
Disadvantages of Pinch Valve
- It cannot be used in high temperature-pressure applications and gas media.
Application of Pinch Valve
- Gauge protection: Install directly in the fluid line or put a tee in the line and attach the valve to the leg of the tee.
- Motion control: Hold rods and shafts in a fixed position. Use for linear or rotational motion control.
- Pneumatic conveying: Control fluidized dry material.
- Pressure relief: Use actuation pressure to close the valve at “normal” operation pressures for the system.
- Surge protection: Modulate surges in pressure or flow rate in a piping system.
- Throttling: Valves can maintain a lower actuation/controlled material pressure differential that is required for complete closure.
- Vacuum receiver: Can eliminate the need for the periodic shutdown of the system to empty a receiver.





 History of a gate valve
History of a gate valve