Types of thermometer – post 1
Types of thermometer
Thermometers design to measure temperatures in industrial and home systems. In this paper, we introduce the standard Types of thermometer in the industry.
mercury thermometer
The mercury-in-glass or the mercury thermometer designed by physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in Amsterdam (1714).
It consists of a bulb containing mercury attached to a glass tube of narrow diameter; the volume of mercury in the tube is much less than the volume in the bulb.
The volume of mercury changes slightly with temperature; the small change in volume drives the narrow mercury column a relatively long way up the tube. The space above the mercury can be filling with nitrogen gas or it may be at less than atmospheric pressure, a partial vacuum.
Alcohol Thermometer
The most common liquid used in common household thermometers used to be mercury, but because of that material’s toxicity, In summary, it replaced by alcohol or ethanol.
Also An alcohol thermometer is a small sealed tube made of glass that has a small hollow bulb on one end and a thin capillary opening running through the length of its center.
The bulb and connected capillary chamber filled partly with ethanol and partly with nitrogen and ethanol vapors.
Enough alcohol places in the bulb so that at normal room temperatures it will extend into the narrow column. Along the length of the column, the tube is graded with several marks showing the temperature of the liquid at certain volumes.
Beckmann Differential Thermometer

The Beckmann differential thermometer used for measuring small differences in temperature, having a readability of around 0.001°C.
This makes it useful for the determination of melting points, boiling points, and calorimetry. Today it is superseded by sensitive digital thermometers using thermocouples, thermistors, etc.
Bimetallic Thermometer
It’s made up of two different metals bonded together, which expand by different amounts as they heat up. As the temperature changes, the bimetallic strip curves more or less tightly (contracts or expands) and the pointer, attached to it, moves up or down the scale.
Galileo thermometer
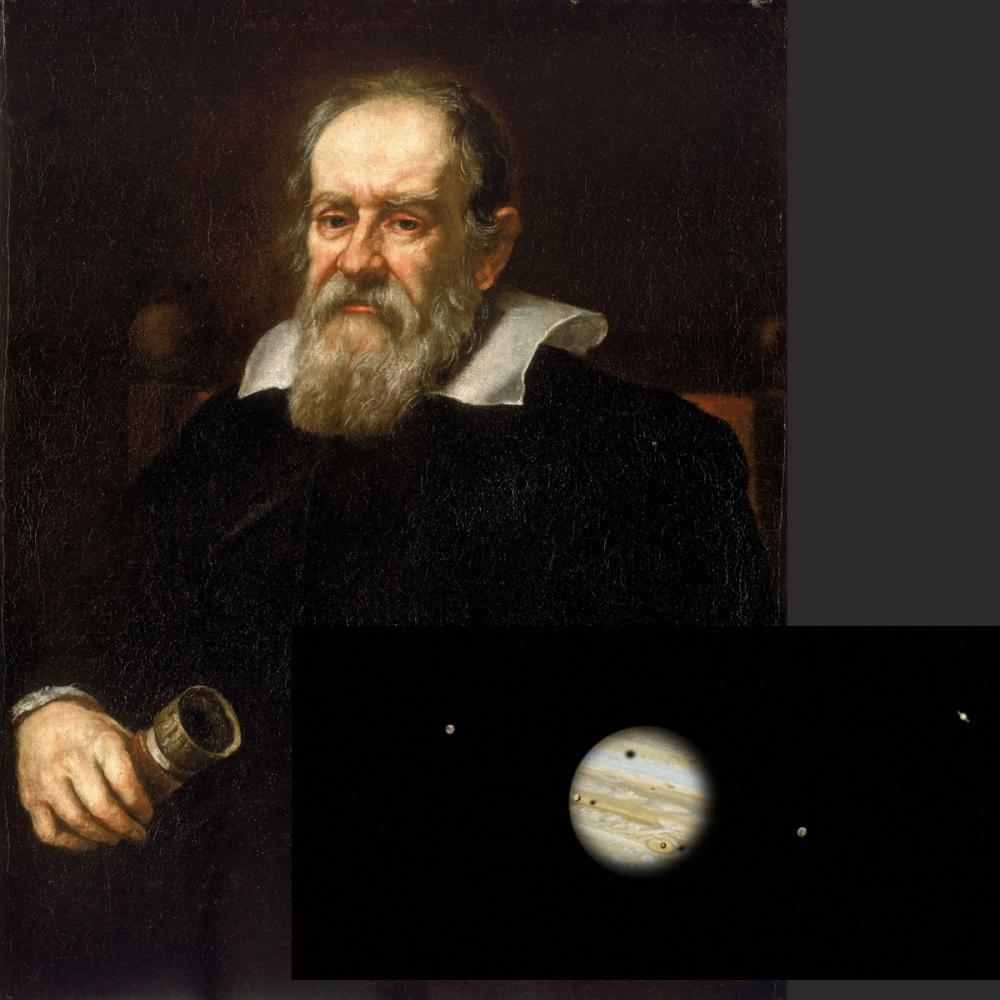

A Galileo thermometer (or Galilean thermometer) is a thermometer made of a sealed glass cylinder containing a clear liquid and several glass vessels of varying density. As the temperature changes, the individual floats rise or fall in proportion to their respective density and the density of the surrounding liquid.
Galileo thermometer used because he discovered the principle on which this thermometer base—that the density of a liquid changes in proportion to its temperature.
Infrared Thermometer
On its most basic design, an infrared thermometer consists of a lens to focus the infrared (IR) energy on to a detector, which converts the energy to an electrical signal that can display in units of temperature after being compensated for ambient temperature variation.
This configuration facilitates temperature measurement from a distance without contact with the object to measure.
As such, the infrared thermometer is useful for measuring temperature under circumstances where thermocouples or other probe type sensors cannot be used or do not produce accurate data for a variety of reasons.
Some typical circumstances are where the object to measure is moving; where the object surround by an EM field, as in induction heating; where the object contain in a vacuum or other controlled atmosphere; or in applications where a fast response is required.
Liquid crystal thermometers
Thermochromic Liquid Crystals (LCs) can be highly temperature sensitive, change to many colors, and are more expensive than leuco dyes.
LCs start black below their temperature range, go through the colors of a rainbow, and back to black again above the temperature range. LCs are reversible in that they can use over and over again. The picture shows an example of a liquid crystal sheet in response to warming.
Popular liquid crystal applications include medical devices, forehead, aquarium and room thermometers, promotional pieces and advertising applications.
Additionally, functional devices such as a propane tank gas level indicator are achieving much notoriety.
Liquid crystal thermometer strips use for thermal mapping and other industrial applications where custom inexpensive temperature monitoring is warranted.
We offer a wide range of liquid crystal thermometers as stock products, but also offer literally thousands of custom products for your label.
- https://www2.humboldt.edu/scimus/HSC.54-70/Descriptions/BckmnThrm.htm
- https://en.wikipedia.org/
- https://www.thomassci.com/scientific-supplies/Mercury-Thermometer
- https://sciencing.com/how-alcohol-thermometers-work-5006550.html
- https://www.explainthatstuff.com/thermometers.html
- https://www.hallcrest.com/color-change-basics/liquid-crystal-thermometers